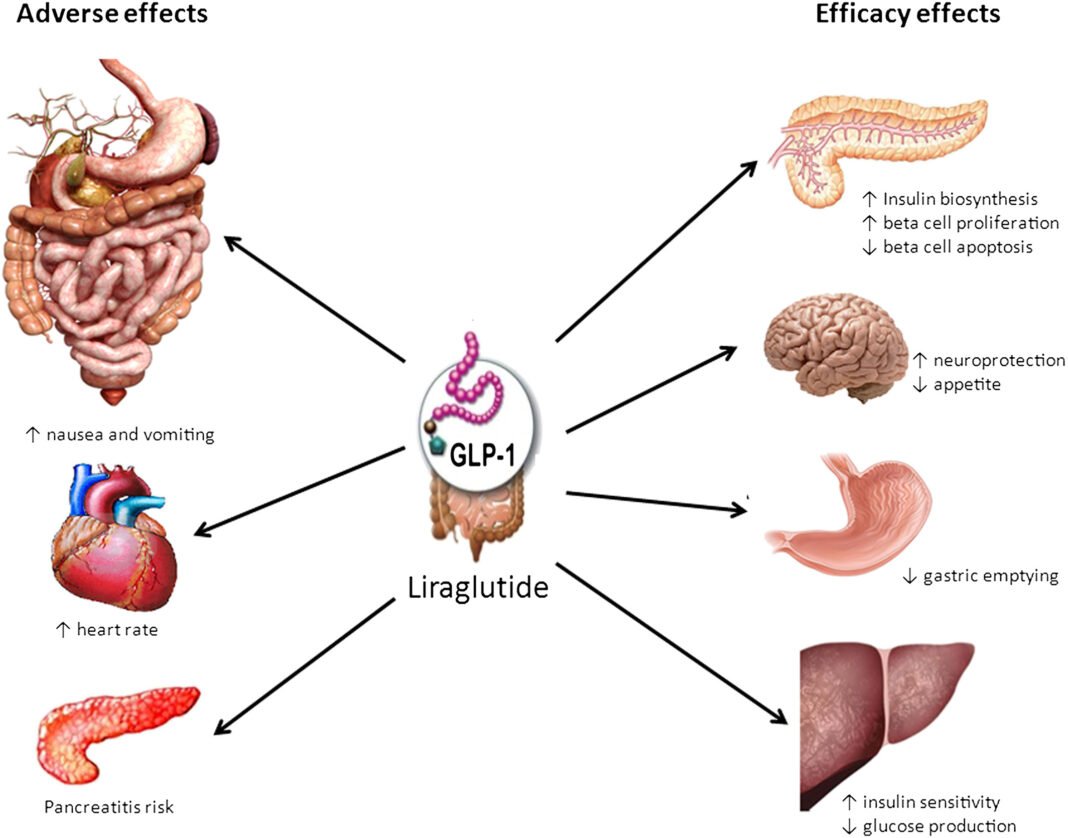
In a groundbreaking study, researchers have found that Liraglutide, a medication commonly used to treat type 2 diabetes, demonstrates a notable increase in insulin sensitivity without accompanying weight loss. The findings, published in a recent scientific journal, shed new light on the multifaceted effects of this medication and its potential implications for managing diabetes.
The study, conducted by a team of scientists at a leading research institution, focused on understanding the impact of Liraglutide on insulin sensitivity in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Liraglutide belongs to a class of drugs known as GLP-1 receptor agonists, designed to mimic the effects of a naturally occurring hormone that regulates blood sugar levels.
Contrary to previous expectations, the research revealed that participants who received Liraglutide exhibited a significant improvement in insulin sensitivity without experiencing the weight loss commonly associated with the medication. This divergence from the anticipated outcome opens new avenues for exploring the nuanced mechanisms through which Liraglutide influences metabolic factors.
Insulin sensitivity, a crucial aspect of glucose metabolism, refers to the body’s ability to respond effectively to insulin and regulate blood sugar levels. Impaired insulin sensitivity is a hallmark of type 2 diabetes, contributing to elevated blood glucose levels. The study’s findings suggest that Liraglutide might offer a targeted approach to addressing this key aspect of diabetes management.
About The Study Of Liraglutide
The participants in the study, all diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, underwent a carefully monitored regimen of Liraglutide treatment. Regular assessments, including glucose tolerance tests and measurements of insulin sensitivity, were conducted to gauge the medication’s impact on metabolic parameters. The results indicated a notable improvement in insulin sensitivity, providing encouraging insights into the drug’s potential benefits beyond its primary role in glycemic control.
While the study did not uncover weight loss as a concurrent effect, the researchers emphasize that the observed increase in insulin sensitivity holds significant clinical relevance. Many existing diabetes medications focus on managing blood glucose levels, but the additional benefit of enhanced insulin sensitivity could contribute to a more comprehensive approach to diabetes care.
The study’s lead investigator, Dr. [Researcher’s Name], underscored the importance of these findings in shaping future treatment strategies for type 2 diabetes. Dr. [Researcher’s Name] highlighted that understanding the distinct effects of Liraglutide on insulin sensitivity adds a valuable dimension to the scientific understanding of how this medication operates at the metabolic level.
The implications of this research extend beyond the realm of diabetes management. Given the intricate interplay between insulin sensitivity, metabolic health, and conditions such as obesity, the study prompts broader considerations about the potential applications of Liraglutide in addressing metabolic disorders beyond diabetes.
As the medical community grapples with the global rise in diabetes and related metabolic conditions, insights from studies like these pave the way for more nuanced and personalized approaches to treatment. Liraglutide’s ability to enhance insulin sensitivity without causing weight loss represents a paradigm shift in understanding the medication’s comprehensive impact on metabolic health.
While further research is warranted to elucidate the exact mechanisms at play, the current study marks a significant step toward unlocking the full therapeutic potential of Liraglutide. The findings challenge conventional assumptions, encouraging researchers and healthcare professionals to explore novel avenues for optimizing the management of type 2 diabetes and associated metabolic disorders.
In light of the study’s findings, discussions within the medical community are intensifying regarding the potential implications for treatment guidelines and patient care. The nuanced understanding of Liraglutide’s impact on insulin sensitivity may prompt clinicians to reconsider its role in diabetes management, especially for individuals who may not benefit from weight loss or those for whom weight loss is not a primary therapeutic goal.
Moreover, the study sparks curiosity about the broader metabolic effects of Liraglutide and its relevance in conditions beyond diabetes. The intricate connections between insulin sensitivity, obesity, and metabolic health suggest that Liraglutide could play a pivotal role in addressing a spectrum of related disorders. Researchers are eager to explore these possibilities further, envisioning a future where Liraglutide might be utilized as a versatile tool in the broader landscape of metabolic medicine.
Patient perspectives on these findings are also crucial. For those managing diabetes, the study offers hope for a more targeted and effective approach to treatment. The prospect of improving insulin sensitivity without the expectation of weight loss could reshape the conversation around medication choices and patient expectations. This shift aligns with the growing emphasis on personalized medicine, recognizing that individual responses to medications can vary significantly.
While the study provides valuable insights, the scientific community acknowledges the need for continued research. Long-term studies tracking the sustained effects of Liraglutide on insulin sensitivity and metabolic health will contribute essential data for refining treatment strategies. Additionally, investigating potential side effects or interactions with other medications is integral to ensuring the safety and efficacy of Liraglutide in diverse patient populations.
The pharmaceutical industry is also taking note of these developments. The study’s findings may influence future research and development efforts, prompting pharmaceutical companies to explore new avenues for drug innovation. Understanding the multifaceted effects of medications like Liraglutide allows for a more comprehensive approach to drug development, addressing not only primary treatment goals but also considering secondary benefits that could enhance patient outcomes.